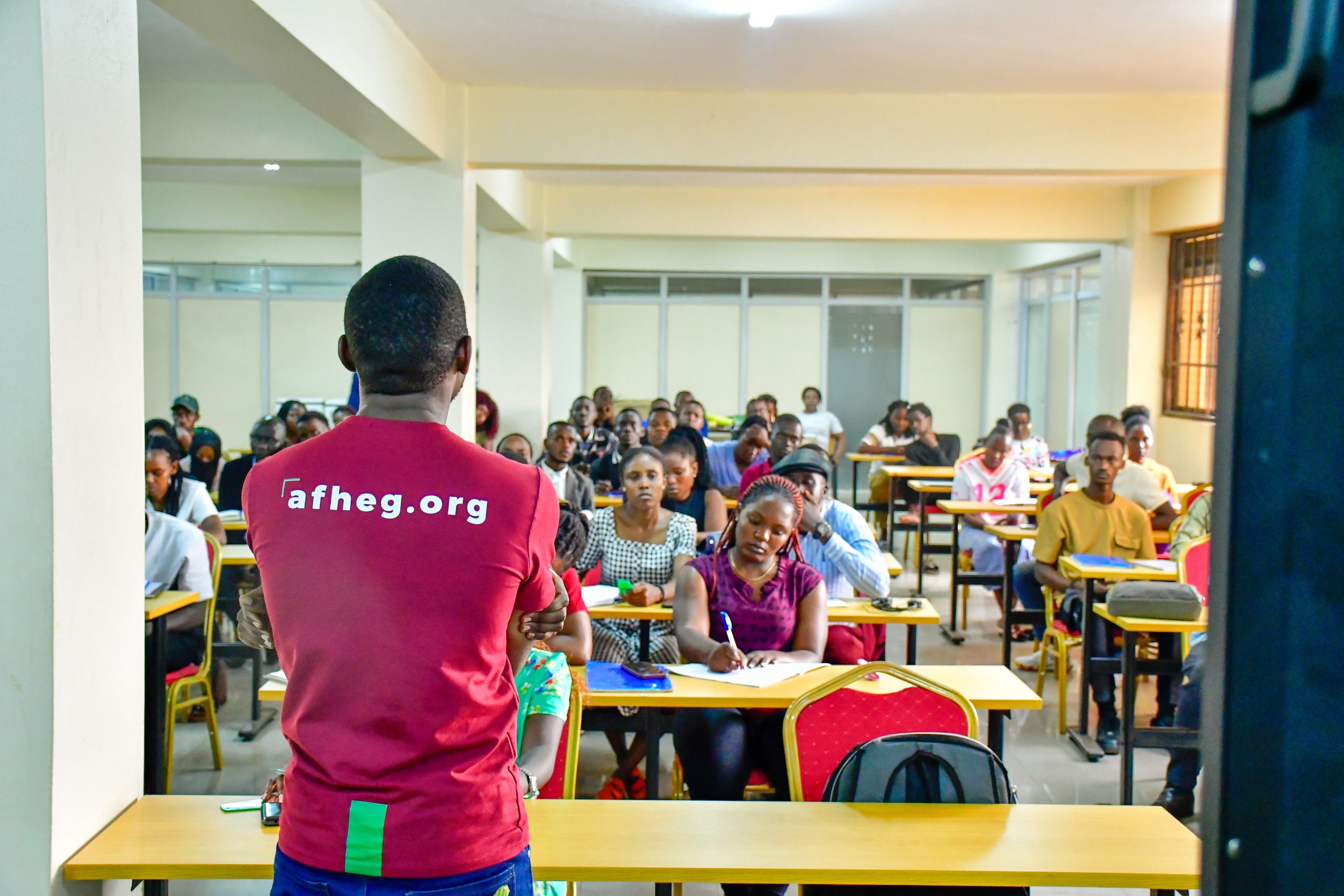
AFHEG Health Communication Training on AMR Training at KIU
AFHEG Health Communication Training took place at Kampala International University (KIU), bringing together over 60 students and lecturers to address antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Organized by the AFHEG Foundation in partnership with KeepersXR, the training focused on bridging the gap between technical health information and community-driven solutions.

The training opened with an introduction to AMR that explained its causes, impacts, and prevention strategies. The lead trainer of AFHEG Foundation, James Nkubuge remarked, “Today we see that understanding AMR is key to stopping self-medication practices that contribute to rising resistance. Knowledge like this has the power to change lives.” Participants were given clear, actionable information that they could share with their communities.
The training opened with an introduction to AMR, highlighting its causes, impacts, and prevention strategies. James Nkubuge, lead trainer at AFHEG Foundation, emphasized the importance of tackling self-medication, stating:
“Understanding AMR is key to stopping self-medication practices that contribute to rising resistance. Knowledge like this has the power to change lives.”
Participants were provided with clear, actionable information to help them communicate health issues effectively within their communities.
A central part of the event was a session on health communication through storytelling. In guided workshops, attendees learned how to convert complex health challenges into relatable narratives. One of the students Namara Hildah noted, “I now have a clear method to share health information in a way that people understand and use to protect their families.” These exercises helped participants move from merely reporting health issues to advocating for solutions that matter.
A core session focused on health communication through storytelling, where students learned to transform complex health challenges into relatable narratives. Namara Hildah, a KIU student, shared her experience:
“I now have a clear method to share health information in a way that people understand and use to protect their families.”
These workshops shifted participants from simply reporting health issues to actively advocating for impactful solutions.

Phillip Andrew Mwebaza, CEO of AFHEG Foundation, added, “Our mission is to empower the next generation of health communicators. Events like this bring together traditional methods and modern technology to create meaningful change. When participants leave equipped with these skills, they carry the promise of healthier communities.” His words echoed the event’s emphasis on practical education and community empowerment.
Phillip Andrew Mwebaza, CEO of AFHEG Foundation, led a session on health communication strategies. He highlighted AFHEG’s mission:
“Our goal is to empower the next generation of health communicators. By merging traditional methods with modern technology, we equip students with skills that create lasting change in their communities.”
This statement reinforced the practical, hands-on approach that defined the training.

To make learning interactive, the training incorporated Superbugs Clash – Kampala Edition, a board game that simulates real-world AMR scenarios. Participants worked in teams, developing critical thinking skills and decision-making strategies.

Rukundo Emmanuel, CEO of KeepersXR, stated, “Integrating VR into our training modules demonstrates how technology can simplify complex health challenges. Our collaboration with AFHEG provides a platform where digital tools directly contribute to health advocacy.” His comments reinforced the role of digital innovation in enhancing the learning experience.
Additionally, KeepersXR introduced immersive Virtual Reality (VR) experiences, showcasing how digital tools can enhance health education. Rukundo Emmanuel, CEO of KeepersXR, explained:
“Integrating VR into training modules shows how technology can simplify complex health challenges. Our collaboration with AFHEG provides a platform where digital tools directly contribute to health advocacy.”

By the conclusion of the training, attendees expressed a clear commitment to advancing health literacy in their communities. Many pledged to apply their new skills in both their professional roles and personal networks, promising to bring a practical, story-driven approach to health communication.By the end of the training, attendees committed to applying their new skills in health advocacy, promising to use story-driven communication to promote health literacy and AMR awareness.
This event underscored the role of interactive learning and digital tools in modern health education. For more on digital health innovation, see the World Health Organization’s information on Antimicrobial resistance.
For additional insights about our approach and further updates on our programs, please visit our Gallery.